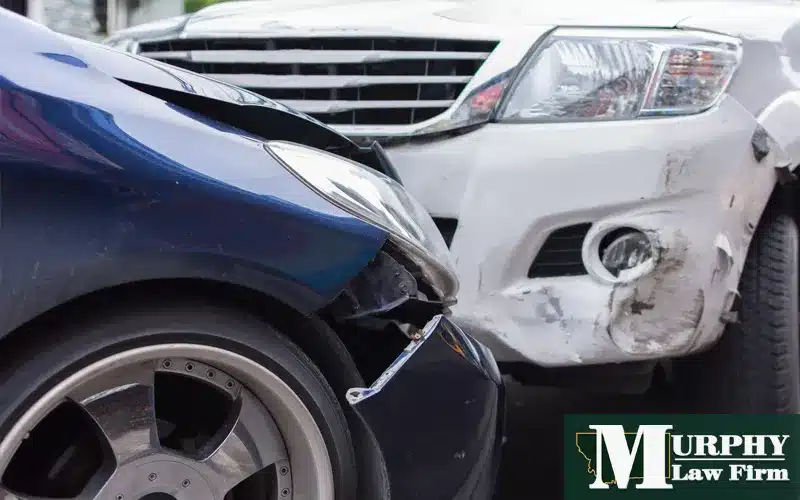
Learn how to prove fault and recover maximum compensation after a head-on collision in Great Falls
Head-on collisions rank among the most perilous and devastating types of car accidents, often resulting in severe injuries or wrongful death. In Great Falls, Montana, navigating the aftermath of such an incident involves not only coping with potential physical and emotional trauma but also confronting the complex process of establishing fault in a personal injury claim.
This article aims to shed light on the inherent dangers of head-on collisions and the crucial steps involved in proving fault within the legal landscape of Montana, providing essential knowledge for those affected by these events to seek justice and compensation for their losses.
Were you injured in a head-on collision in Montana?
The experienced Great Falls car accident attorneys at Murphy Law Firm
can help you recover the compensation you deserve.
Get started today by scheduling a free consultation.
What does it mean when a collision is head on?
When a collision is described as “head on,” it means that 2 vehicles have collided with each other front to front. This type of accident typically occurs when one of the vehicles strays from its designated lane into oncoming traffic, leading to a direct impact between the front ends of both vehicles.
Head-on collisions are considered to be among the most dangerous and potentially deadly types of road accidents due to the high levels of force and energy involved, often resulting in catastrophic injuries or fatalities for the occupants of the vehicles.
What happens during a head-on collision?
During a head-on collision, 2 vehicles crash directly into each other with their front ends, typically while moving toward one another. This type of collision often results in a sudden and violent impact, causing significant deformation of the vehicle structure, especially in the front crumple zones designed to absorb the force of the impact.
The occupants may experience a sudden jolt or be thrown forward against seat belts, airbags, or even the dashboard and windshield if restraints fail or are not used. This can result in a range of injuries, from minor cuts and bruises to more severe injuries such as fractures, head injuries, spinal injuries, and internal damage.
The severity of injuries often depends on factors such as:
- The speed of the vehicles at the time of impact
- The use of seat belts and airbags
- The angle of the collision
- The physical condition of the occupants
In addition to physical injuries, these collisions can also result in significant psychological trauma, including shock, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), affecting the victims’ ability to drive or even ride in vehicles comfortably afterward.
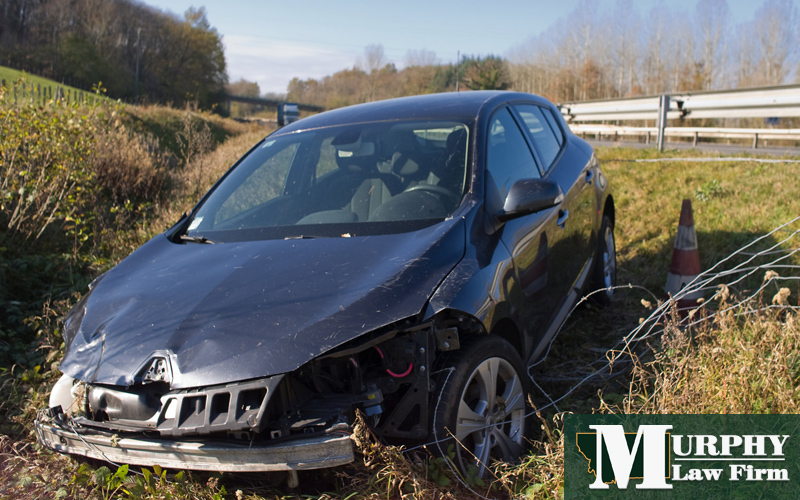
The vehicles involved also typically suffer extensive damage, often resulting in total loss due to the high energy involved in front-to-front impacts.
What To Do After A Car or Truck Accident in Montana
Learn the 5 steps to take after an auto accident in Montana to protect your right to compensation.
How serious is a head-on collision?
Head-on collisions are among the most severe types of vehicle accidents, contributing significantly to traffic-related fatalities in the United States.
According to the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), such collisions represent the most harmful event in about 14% of all U.S. traffic deaths annually. Furthermore, they account for 27% of all fatalities resulting from roadway departures (RwD), in which a vehicle crosses the centerline or otherwise veers off its path.
In 2021 alone, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) reported that head-on crashes led to 4,259 fatalities and 77,399 nonfatal injuries on U.S. roads.
These statistics underscore the serious nature of head-on collisions and their substantial impact on road safety.
What is the main cause of death in a head-on collision?
The main cause of death in a head-on collision typically results from the severe impact and rapid deceleration that occur when 2 vehicles collide front to front.
This intense force can lead to catastrophic injuries such as traumatic brain injuries, internal bleeding, and major organ damage. The direct impact often causes occupants to be forcefully thrown against vehicle interiors, even with seatbelts and airbags, exacerbating the likelihood of fatal injuries.
Additionally, the high energy transferred between the colliding vehicles can lead to structural collapse of the passenger compartment, further increasing the risk of fatal outcomes for the occupants.
Who is wrong in a head-on collision?
Proving fault in a head-on collision requires a detailed investigation that looks into the circumstances leading up to the accident. Investigators will examine evidence such as skid marks, vehicle damages, dashcam footage, traffic signals, and road conditions. They will also review witness statements and police reports to understand the events leading up to the collision.
Key factors considered include:
- Violation of traffic laws. Investigators will determine if either driver violated traffic laws, such as speeding, running a red light, texting and driving, or driving under the influence, which contributed to the collision.
- Wrong-way driving. If one vehicle was going the wrong way on a roadway, that driver is typically found at fault for the head-on collision.
- Lane departures. Fault may be attributed to the driver who veered out of their lane, whether due to distraction, impairment, or loss of control of the vehicle.
- Road conditions. Sometimes, external factors like poor road design, inadequate signage, bad weather, or other hazardous conditions can contribute to a head-on collision, potentially implicating other parties beyond the drivers.
- Vehicle conditions. Fault can also be influenced by the condition of the vehicles involved, especially if mechanical failure contributed to the accident.
Once the investigation is complete, fault is assigned based on which party’s actions or negligence predominantly caused the accident. However, sometimes both parties share some blame for the accident.
Montana Statute of Limitations
When is it too late to file a personal injury, car accident, workers’ comp or wrongful death claim?
What happens if both drivers are at fault in a Montana car crash?
In Montana, which uses a modified comparative fault system, if drivers share fault in a head-on collision, the compensation each driver can receive for damages will be reduced by their respective percentages of fault.
However, if a driver is found to be 51% or more at fault, they are barred from recovering any damages.
Let’s say, for example, that Driver A and Driver B are involved in a head-on collision. After the investigation, Driver A is found to be 40% at fault for speeding, while Driver B is found to be 60% at fault for veering into the wrong lane.
In this scenario, Driver A can recover damages because they are less than 51% at fault. However, the total amount of damages they can receive will be reduced by their percentage of fault. So, if Driver A had $100,000 in damages, their final compensation in this scenario would be $60,000, reflecting a 40% reduction due to their assigned fault.
Conversely, Driver B, who is more than 51% at fault, would not be eligible to recover any damages from Driver A due to Montana’s modified comparative fault rules. This system ensures that compensation is awarded in a manner that reflects each party’s contribution to the accident while also discouraging negligent driving behaviors.
Get help from an experienced Montana car accident attorney after a head-on crash
Due to Montana’s comparative fault system, it’s crucial for drivers to seek the help of an experienced attorney to protect their rights and minimize their liability after an accident.
At Murphy Law Firm, our skilled car accident attorneys boast over 75 years of collective experience in securing rightful compensation for injured drivers in Great Falls, Montana. Reach out to us today for a free case evaluation, and let us help you on your road to recovery.